
We specialize in customized PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) coating solutions tailored to meet your specific requirements. Whether you need enhanced durability, improved performance, or a unique aesthetic finish, our expert team works closely with you to develop the perfect coating solution for your application.
✅ Custom Colors & Finishes – Choose from a wide range of colors, including gold, rose gold, black, chrome, and more, with matte, glossy, or textured finishes.
✅ Material Compatibility – Our coatings are suitable for metals, plastics, ceramics, and other substrates, ensuring optimal adhesion and performance.
✅ Performance Enhancements – Improve hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and friction reduction to extend the lifespan of your products.
✅ Industry-Specific Solutions – We provide coatings for automotive, medical, luxury goods, cutting tools, and more, ensuring precision and functionality.
✅ Eco-Friendly & Sustainable – Our PVD coating process is environmentally friendly, using no harmful chemicals or pollutants while delivering superior results.
Overview Of PVD Coating
PVD coating is an environmentally friendly vacuum coating process. Due to its excellent wear and corrosion resistance, PVD is often used to give parts enhanced performance and a brilliant decorative finish. PVD coating processes are common in industrial, non-industrial, and cosmetic applications. It is a very important surface finishing process in the modern manufacturing industry.
PVD coating is a process that involves depositing a thin layer of material onto the surface of a substrate using a physical vapor deposition (PVD) process. The material is vaporized and then deposited onto the substrate in a vacuum chamber, forming a thin and uniform coating. The coating material to be vaporized is referred to as a “target” or “source material.” Source Materials can include metals, alloys, ceramics, compositions, and anything from the periodic table, depending on the end product.
Because of their high hardness, wear resistance, and low friction properties, PVD coatings are well-suited for various applications, such as the automotive, aerospace, and medical industries. In addition, PVD coatings are often used in manufacturing tools and equipment to improve their durability and performance. Some materials that can be PVD-coated include metals, ceramics, and polymers.
4 STEPS OF PVD COATING:
Cleaning: The first step in the PVD coating process is cleaning the substrate, which is the material to which the coating will be applied. This involves using various methods, such as mechanical or chemical cleaning, to remove any dirt, debris, or other contaminants from the surface of the substrate. This is important because any impurities on the substrate’s surface can affect the coating’s quality.
Pretreatment: The next step is pretreatment, which involves subjecting the substrate to a process that improves the adhesion of the coating. This can include processes such as anodizing or plasma etching, which create a rough surface on the substrate that allows the coating to adhere more easily.
Coating: The third step is the actual PVD coating process, which involves heating a source material, such as a metal or ceramic, to a high temperature until it evaporates. The vaporized material is then deposited onto the substrate, forming a thin, uniform layer. The coating process is typically carried out in a vacuum chamber, which helps to prevent the vaporized material from reacting with any air or other gases.
Quality Control: After the coating has been applied, it is inspected to ensure that it meets the desired specifications. This may involve various tests, such as measuring the thickness of the coating or testing its hardness and durability.
Finishing: The final step is finishing, which involves subjecting the coated substrate to additional processes, such as polishing or buffing, to improve its appearance or performance. This can include processes such as surface finishing or coloration, which can enhance the visual appeal of the coated product.
4 COMMON TYPES OF PVD COATING PROCESS:
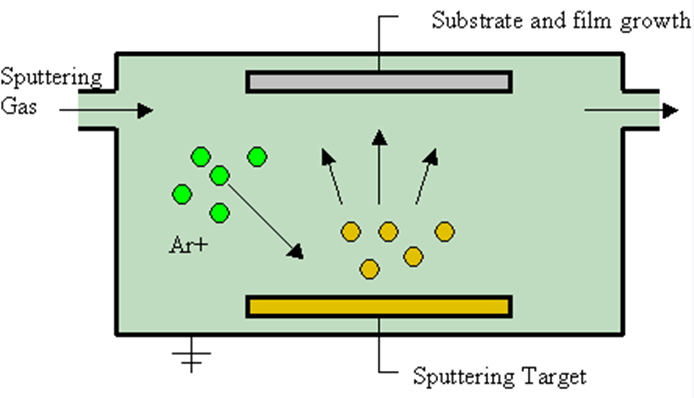
Sputter Coating
Sputter coating is a PVD coating process in which a target material, such as a metal or ceramic, is bombarded with high-energy ions. This causes the target material’s atoms to be ejected or sputtered from the surface and then deposited onto the substrate. The ions used in sputter coating can be either positive or negative, and the type of ions used can affect the properties of the coating.
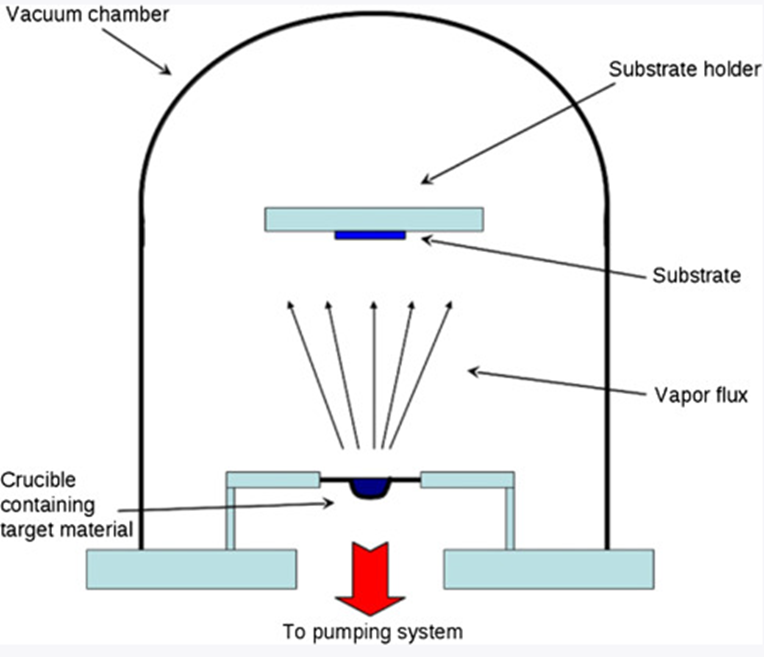
Thermal Evaporation
Thermal evaporation is a PVD coating process in which source material is heated until it evaporates. The vapor is then deposited onto the substrate, forming a thin, uniform layer. This process is often used for coating materials sensitive to ion bombardment or applications requiring a high degree of control over the coating process.
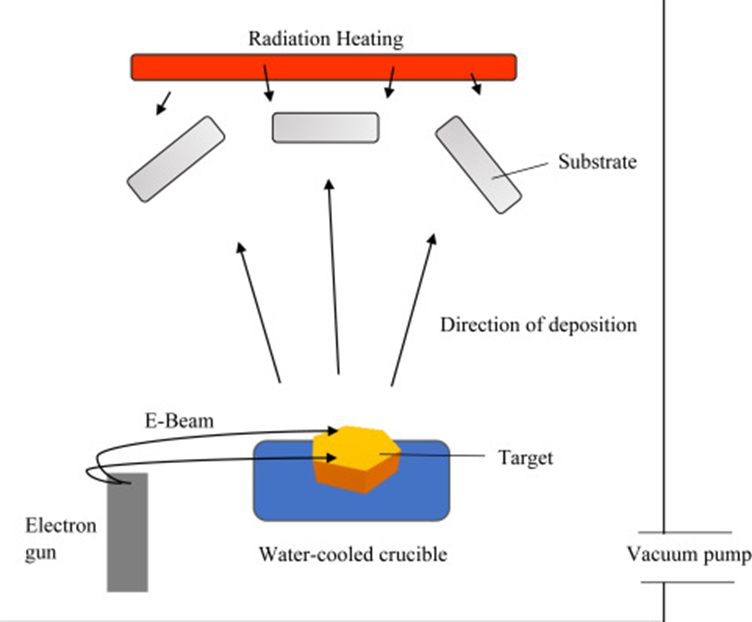
Electron Beam Evaporation
Electron beam evaporation is a PVD coating process in which a focused beam of electrons is used to heat and evaporate the source material. The vapor is then deposited onto the substrate, forming a coating. This process allows for more precise and controlled deposition of the coating material, which makes it useful for applications where a high degree of accuracy is required.
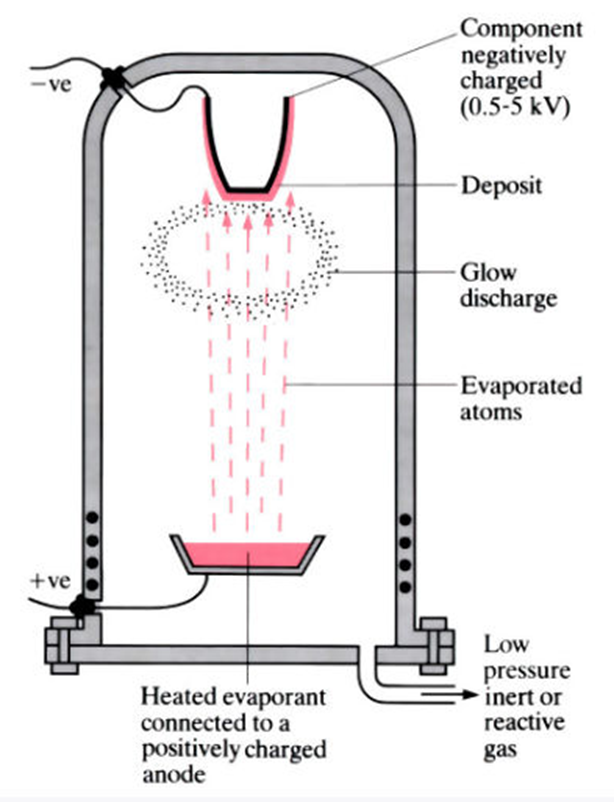
Ion Plating
Ion plating is a PVD coating process in which a gas containing atoms of the coating material is introduced into the vacuum chamber. The gas is ionized, and the ions are then accelerated and directed toward the substrate, where they are deposited to form a coating. This process allows for a more uniform and consistent coating than other PVD processes, making it useful for applications requiring a high degree of uniformity.
 WhatsAPP
WhatsAPP